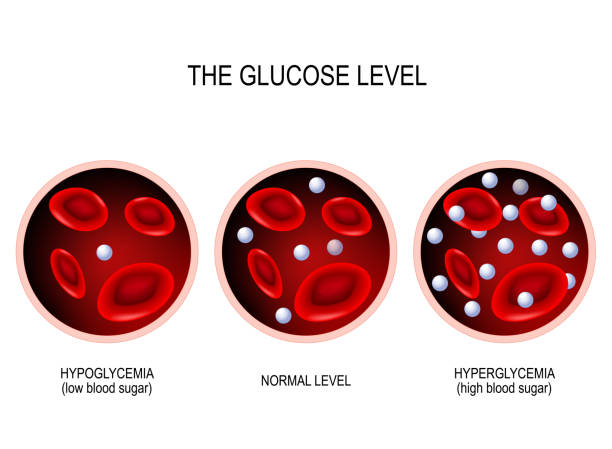
Diabetes mellitus, commonly known as diabetes, is a group of metabolic disorders that affect how your body processes glucose (sugar). Glucose is essential for energy production, but when its regulation goes awry, it can lead to serious health complications. Let’s delve into the different types of diabetes, their causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Types of Diabetes Mellitus
Type 1 Diabetes (Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus or IDDM)
Summary
Type 1 diabetes typically begins in childhood and results from an autoimmune attack on the pancreas. The pancreas fails to produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels.
Causes:
Type 1 diabetes occurs when the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. The exact cause of this autoimmune response is not fully understood, but it is believed to involve a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
- Autoimmune destruction of the pancreatic islets of Langerhans.
- Genetic predisposition.
Symptoms:
- Excessive thirst and hunger.
- Frequent urination.
- Unexplained weight loss.
- Fatigue.
- Blurred vision.
Diagnosis:
- Blood tests, including the A1C test (estimates average blood sugar levels over the past three months).
Treatment:
- Insulin injections (syringes, insulin pens, or pumps).
- Regular blood sugar monitoring.
- Lifestyle modifications (healthy diet, exercise)
Type 2 Diabetes (Non-Insulin-Dependent Diabetes Mellitus or NIDDM)
Summary
Type 2 diabetes usually develops after age 40 and is associated with insulin resistance. Cells become less responsive to insulin, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Causes:
- Genetic factors.
- Sedentary lifestyle.
- Obesity.
- Poor diet.
Symptoms:
- Similar to type 1 diabetes but often milder.
- Slow-healing wounds.
- Tingling or numbness in extremities.
Diagnosis:
- Fasting blood sugar test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test.
- A1C test.
Treatment:
- Lifestyle changes (weight loss, exercise, healthy eating).
- Oral medications (metformin, sulfonylureas).
- Insulin therapy if needed.
Type 3 Gestational Diabetes
Summary
Occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth.
Causes
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy.
Symptoms
- Often asymptomatic.
- Increased thirst and urination.
Diagnosis
- Glucose challenge test.
- Oral glucose tolerance test.
Treatment
- Blood sugar monitoring.
- Diet modification.
- Insulin if necessary.
Conclusion
Diabetes is a complex condition that requires lifelong management to prevent complications and maintain overall health. By understanding the causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options for each type of diabetes, individuals can take proactive steps to manage their condition effectively. Regular monitoring, healthy lifestyle choices, and adherence to treatment plans are essential for controlling blood sugar levels and minimizing the risk of complications associated with diabetes. If you have any concerns or questions about diabetes, consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and support. With proper management and care, individuals with diabetes can lead fulfilling and healthy lives.
With proper care, education, and lifestyle adjustments, most people with diabetes can live full, active lives. Early diagnosis is key, so see your doctor promptly if you experience any potential symptoms of diabetes.
Taking Charge of Your Health
Living with diabetes requires vigilance and self-care. Here are some resources to get you started:
- American Diabetes Association: https://diabetes.org/
- National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases: https://www.niddk.nih.gov/
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: https://www.cdc.gov/diabetes/index.html

One thought on “Diabetes Mellitus: Types, Causes, Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment”