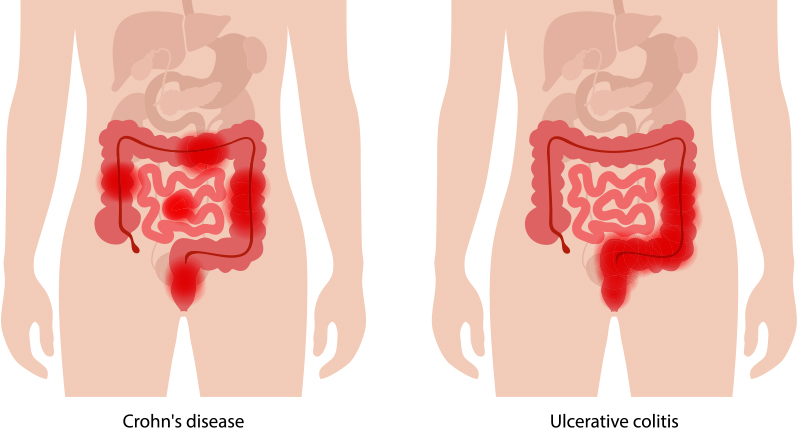
Summary of Crohn’s Disease
Crohn’s disease is a chronic inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) that causes inflammation in your digestive tract. This inflammation can lead to a variety of unpleasant symptoms that can significantly impact your daily life. While there’s no cure for Crohn’s, there are effective treatments available to manage symptoms and maintain a good quality of life.
What Causes of Crohn's Disease?
The exact cause of Crohn’s disease remains unknown, but researchers believe several factors may play a role:
- Autoimmune Response: In some cases, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy tissues in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation.
- Genetics: Having a close relative with Crohn’s disease increases your risk of developing it.
- Environmental Factors: Certain environmental factors, such as smoking or exposure
- An abnormal immune system response that attacks healthy bacteria in the digestive tract, leading to inflammation
- Genetics, as Crohn’s disease tends to run in families
- Environmental triggers like bacteria, viruses, diet, smoking, and stress
Symptoms of Crohn's Disease Text Here
Crohn’s disease can cause a variety of symptoms, which can vary in severity and may come and go over time. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent diarrhea
- Abdominal pain and cramping
- Rectal bleeding
- Fatigue
- Unintended weight loss
- Reduced appetite
- Fever
- Mouth sores
- Joint pain
- Skin problems
Diagnosis of Crohn's Disease
Diagnosing Crohn’s disease can involve several tests, including:
- Blood tests to check for anemia or inflammation
- Stool tests to rule out infections
- X-rays or CT scans to visualize the intestines
- Endoscopy, a procedure where a thin, flexible tube with a camera is inserted into the digestive tract to examine for inflammation and ulcers
Treatment Options for Crohn's Disease
While there is no cure for Crohn’s disease, various treatment options are available to help manage symptoms, reduce inflammation, and prevent complications. Treatment strategies may include:
- Medications: Anti-inflammatory drugs, immunosuppressants, biologic therapies, antibiotics, and other medications may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and suppress the immune system.
- Nutritional therapy: Some people with Crohn’s disease may benefit from dietary modifications or nutritional supplements to manage symptoms and improve nutrient absorption.
- Lifestyle changes: Quitting smoking, adopting a healthy diet, managing stress, and getting regular exercise can help alleviate symptoms and improve overall health.
- Surgery: In severe cases or when complications arise, surgery may be necessary to remove damaged portions of the digestive tract or repair fistulas, strictures, or other abnormalities.
In some cases, surgery may be required to remove a damaged or diseased portion of the intestine. Diet changes, like a low-residue or low-fiber diet, can also help control symptoms.
There is no cure for Crohn’s disease, but with proper treatment and management, many people are able to control their symptoms and live full lives. If you experience persistent digestive problems, see your doctor promptly for an evaluation.

One thought on “What is Crohn’s Disease? Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, and Treatment”